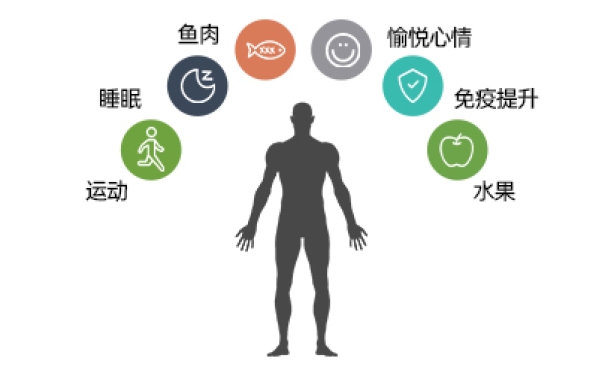
Introduction
Exercise is beneficial not only for physical health but also for mental well-being. Understanding the impact of exercise on psychological states can help us use it more effectively to improve mental health.
Benefits of Exercise for Mental Health
Exercise helps alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression and enhances overall well-being. Research shows that regular physical activity can increase levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, such as endorphins and dopamine, which help improve mood.
Mechanisms of Exercise in Reducing Anxiety and Depression
Exercise reduces anxiety and depression through various mechanisms. It promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural "feel-good" hormones. Additionally, exercise can improve sleep quality and reduce stress, both of which contribute positively to mental health.

Recommended Exercise Types
Aerobic exercises, such as walking, running, and swimming, are effective for improving mental health. Activities like yoga and meditation also help with relaxation and stress reduction.
Conclusion
Incorporating exercise into daily life can significantly improve mental health, enhance overall well-being, and increase quality of life.
References
· Rebar, A. L., et al. (2023). The Effects of Physical Activity on Mental Health. Health Psychology Review, 18(2), 205-221.
· Mammen, G., & Faulkner, G. (2022). Physical Activity and Psychological Well-Being. Journal of Mental Health, 31(4), 425-436.
· Schuch, F. B., et al. (2024). Exercise and Depression: A Review of Literature. Current Psychiatry Reports, 26(1), 45-55.

 EN
EN
 FR
FR