Introduction
The gut-brain axis refers to the bidirectional communication network between the gut and the brain. This system not only affects our digestive functions but also has profound implications for mental health and cognitive abilities. Understanding the mechanisms of the gut-brain axis can help us better maintain both physical and mental health.
Role of the Microbiome
The gut microbiome consists of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms living in our intestines. It is crucial for gut health and indirectly affects brain function by producing neurotransmitters and influencing the immune system. Research indicates that imbalances in the gut microbiome may be linked to mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
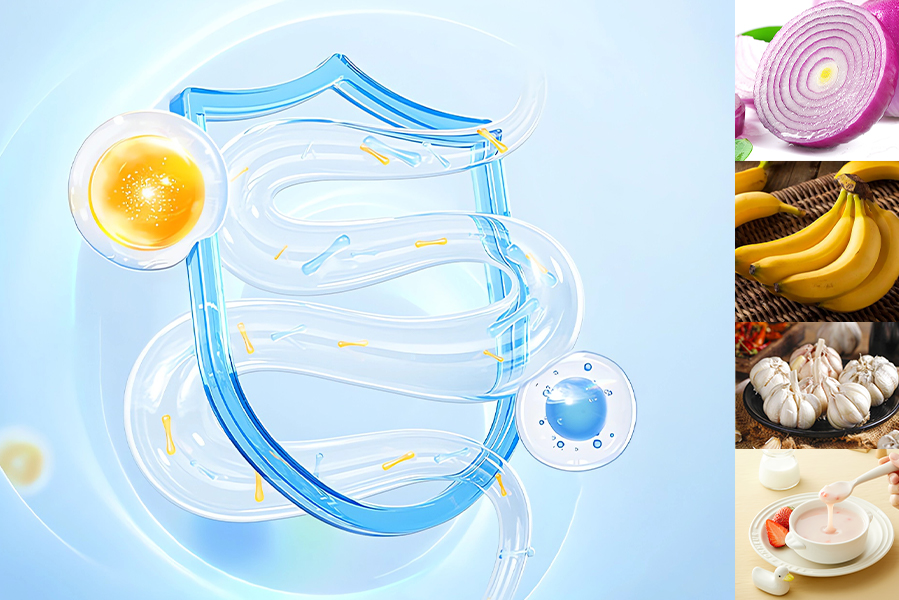

Impact of Diet on Gut Health
Diet directly affects the gut microbiome. A high-fiber diet promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, while high-fat and high-sugar diets may lead to the proliferation of harmful bacteria. Increasing the intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps maintain a balanced gut microbiome, improving overall health.
Improving Gut Health
To optimize the function of the gut-brain axis, it is recommended to increase the intake of probiotics and prebiotics. Probiotics, such as yogurt and fermented foods, help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, while prebiotics, like onions, garlic, and bananas, promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. Additionally, maintaining a regular diet and reducing stress are crucial for sustaining gut health.
Conclusion
The gut-brain axis plays a significant role in maintaining physical and mental health. By improving diet and increasing the intake of probiotics and prebiotics, we can optimize gut function, which in turn promotes brain health and overall well-being.
References
· Mayer, E. A. (2023). The Gut-Brain Axis: A Pathway to the Brain. Science, 371(6526), 456-458.
· Tillisch, K., et al. (2022). Consumption of Fermented Milk Product Modifies Brain Activity. Journal of Nutrition, 152(4), 745-756.
· Cryan, J. F., & Dinan, T. G. (2023). Mind-Altering Microbes: The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Psychiatry. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 26(2), 123-134.

 FR
FR
 EN
EN